I am often asked to restore files on fileservers and also look for user who deleted files. By default there is no auditing for files enabled on fileservers. I will write how I do enable it and how it works for me.
First of all you need to enable audit policy Audit object access. This audit policy handles auditing for files, registry keys, shares, … To enable this audit policy you need to set it in GPO Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Local Policies – Audit Policy – Audit object access and set it to Success, Failure.
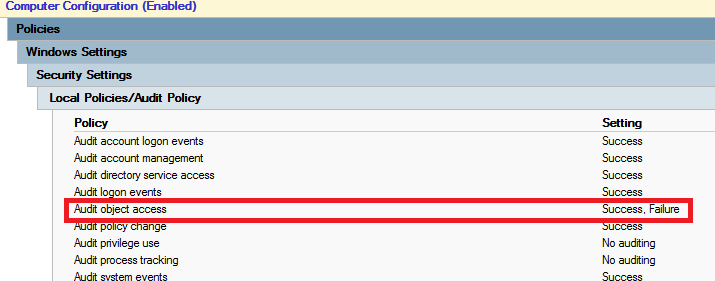
This audit policy enables auditing for lots of objects to audit. I want to audit only File System. To find out what audit policy settings are applied on computer use following commnad auditpol.exe /get /category:*. To enable only wanted auditing I have dumped settings using auditpol.exe command and set same auditing in GPO, but under Object Access I just enabled File System auditing. You can set this settings under Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Advanced Audit Configuration.
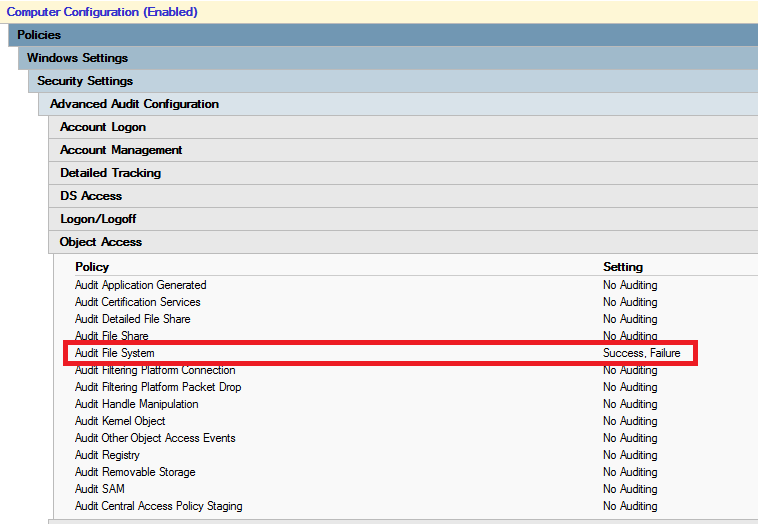
Now you need to setup Auditing on whole Disks or Folders:
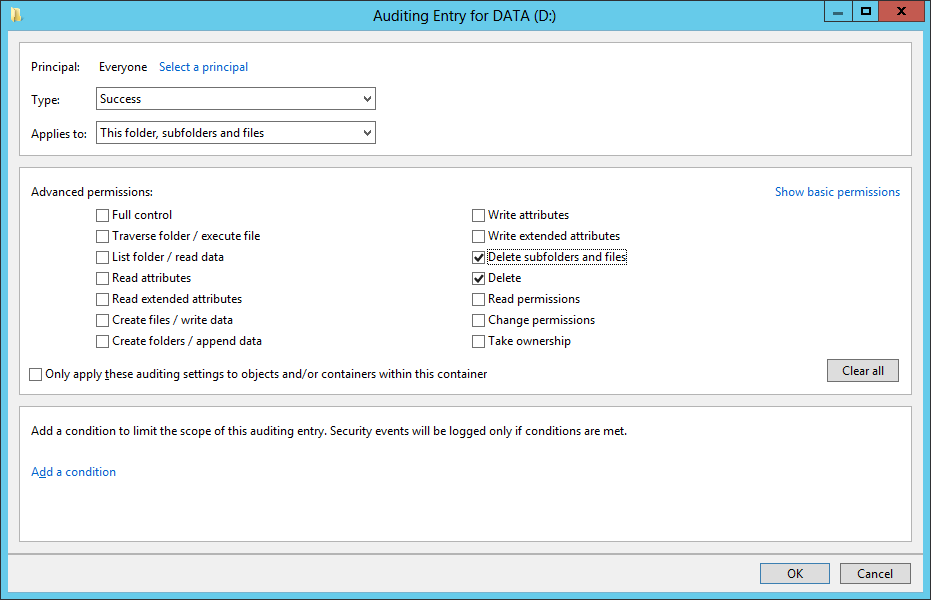
When these settings in GPOs are applied there are new events in security event log. We need to look for event number 4659 and make some reporting out of it. I’ve created powershell script which I run every day right after midnight and it creates HTML report and also CSV files which can be used in some powershell manipulation. Here is a powershell script:
#
# Get-DeletedFileLog
# This function gets events 4659 about delted files and generate HTML reports
#
#
# Declaration
#
[datetime]$Yesterday = ((Get-Date) - (New-TimeSpan -Day 1)).date
[datetime]$Today = (Get-Date).date
[int]$EventID = 4659
[string]$Path = "D:\Logs\Deleted Files"
[int]$Limit = (Get-Date).AddDays(-180)
Try
{
#
# Get events from security eventlog
#
[array]$EventList = Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';Id=$EventID;StartTime=$Yesterday} -Oldest -ErrorAction Stop
#
# Extend Event by XML data fields
#
foreach ($Event in $EventList)
{
$EventXML = [xml]$Event.ToXML()
For ($i=0; $i -lt $eventXML.Event.EventData.Data.Count; $i++)
{
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name DateFileDeleted -Value $Event.TimeCreated
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name UserName -Value $EventXML.Event.EventData.Data[1].'#text'
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name DeletedFile -Value $EventXML.Event.EventData.Data[6].'#text'
}
}
#
# Generate HTML report
#
$EventList | Select DateFileDeleted, UserName, DeletedFile | ConvertTo-Html | Out-File "$($path)\$($Today.Year)$($today.Month)$($Yesterday.Day)_DeletedFiles.html"
$EventList | Select DateFileDeleted, UserName, DeletedFile | ConvertTo-Csv | Out-File "$($path)\$($Today.Year)$($today.Month)$($Yesterday.Day)_DeletedFiles.csv"
}
Catch
{
# If there is a problem
Write-Host "No events $EventID to record."
}
#
# Remove old reports
#
Get-ChildItem -Path $Path -Recurse -Force | Where-Object { !$_.PSIsContainer -and $_.CreationTime -lt $Limit } | Remove-Item -Force
# EOF
This script also cleans up files older than 180 days. In HTML file you can see when, who and what deleted. I didn’t excluded files started with “~”, which are also known as temporary Office files, which are created during opening Office documents. This is because now I know who opened which files and when.
Enjoy,
At one of our customers we deployed RDS RemoteApp server farm. Customer bought thin clients HP T510. When they connected to RemoteApp using Windows XP and Windows 7 on normal computers there were no problems with RemoteApps. When they connected to RemoteApp using Windows 7 Embedded on thin clients, they had problems with RemoteApp windows. RemoteApp windows were not displayed right. There was one extreme problem: User opened Microsoft Outlook, opened message and pressed Reply. Starte to type, but no characters were displayed. When you clicked on some part of the window all the text appeared. So RDP client sent all key strokes to RDP server, but RDP client didn’t refresh content of the window.
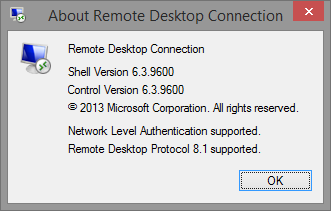
After some investigation I found out that Windows XP and Windows 7 had RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported), but Windows 7 Embedded had only 6.2.9200 (RDP 8.0 supported). I’ve tried to google for some path or some HP image with RDP 8.1 for Windows 7 Embedded. No success. When you look on Remote Desktop Service Blog website, you can even find informaction that there is no RDP 8.1 for Windows Embedded.
But I found five hotfixes which are required for Windows 7 Emedded to have RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported):
- KB2574819-v2-x86
- KB2592687-x86
- KB2857650-x86
- KB2830477-x86
- KB2913751-x86
When you install all those updates you need to reboot machine and you will have nice RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported):
That’s all for now,
Sometimes I need to run some command on bunch of computers. So I’ve created little bit more advanced function to be able to run script block on computers list created from domain:
<#
.Synopsis
This function provides you way to run scriptblock on remote machines in the domain.
.DESCRIPTION
This function is extension to Cmd-Let Invoke-Command. This function lists computer names in domain
based on ADSearchBase and Filter parameters. In invoke scriptblock on those computers in the list.
.EXAMPLE
To restart service "Windows Time" on all machines in domain:
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase "DC=domain,DC=local" -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
.EXAMPLE
To restart service "Windows Time" on all machines which containt number 7 in name:
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase "DC=domain,DC=local" -Filter 'Name -like "*7*"' -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
#>
Function Invoke-CommandOnADComputers
{
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True,ConfirmImpact='Low')]
Param
(
# This is Active Directory Search Base to limit selection for computer accounts in domain.
# It can be for example "OU=Computers,OU=Company Name,DC=domain,DC=local"
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]
$SearchBase,
# Active Directory filter to merge your computer selection in to the detail.
# It can be for example 'Name -like "Desktop*"'
[string]
$Filter = "*",
# This is scriptblock which should be run on every computer.
# For example { Restart-Service W32Time; }
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[scriptblock]
$ScriptBlock
)
Begin
{
#
# Get list of computer accounts
#
Write-Verbose "Getting list of computer from $ADSear"
try
{
[array]$ADComputersList = Get-ADComputer -SearchBase $SearchBase -Filter $Filter -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch
{
Write-Error -Message "Couldn't search in $SearchBase" -ErrorAction Stop
}
#
# Write number of found computers
#
Write-Host "Found $($ADComputersList.Count) computers"
#
# If in debug, write list of computers
#
Write-Verbose "List of machines:"
If (!$PSDebugContext)
{
foreach ($item in $ADComputersList)
{
Write-Verbose " $($item.Name)"
}
}
Write-Verbose "Done with domain computer list"
}
Process
{
#
# Let's invoke command on remote computer
#
foreach ($ADComputer in $ADComputersList)
{
Write-Host $ADComputer.Name
try
{
Write-Verbose "Invoking scriptblock on computer"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $ADComputer.Name -ScriptBlock { $ScriptBlock } -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Host " Scriptblock invoked successful."
}
catch
{
Write-Host " Scriptblock invoked UNSUCCESSFUL."
}
}
}
}
You can run it using
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase “DC=domain,DC=local” -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
and it will read all computer accounts from domain and restart Windows Time service.
Enjoy,
This year VMware granted me a non-technical certification vExpert. I helped out on VMWare Thinapp forum.

I’m so happy 😉
Sometimes when you work on linux in bash you don’t want to leave commands in bash history (.bash_history). Easy way to clean it up it’s to run following command:
HISTSIZE=0
Now your bash history will be not accessible and not saved when you logoff.
If you want to know if your computer is ready to host Hyper-V role you can check it quickly using old command systeminfo.exe with new feature. This new feature is in systeminfo.exe which is included in Windows 8 and higher and Windows Server 2012 and higher.
When you run it you can see the last output lines about Hyper-v Requirements:
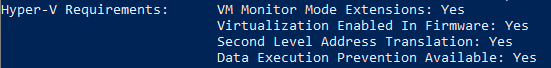
That’s all for today,
I just found one cool utility. It’s called clip.exe. You can use this utility to input the content from pipline into clipboard and then paste the content of clipboard where ever you want.
Here a example:
ipconfig /all | clip
When you run this all the output from command “ipconfig /all” is stored into windows clipboard. Now you can Paste (CTRL+V) this into any application you want.
When you want to read the content of any file into windows clipboard you can use following command:
clip < C:\kukuc.txt
This cool utility came with Windows Server 2003 (not in Windows XP) and stayed there until Windows 8 and Windows Server 2012 R2.
Have a good day,
I’m creating couple powershell scripts which I use in my work. I want to share couple of them with you. So here is a script which look for domain computers and then check who is logged on those online machines.
$ADSearchBase = "OU=Computers,DC=domain,DC=local"
$ADFilter = "*"
Function Get-LoggedUsersOnComputers
{
$ADComputersList = Get-ADComputer -SearchBase $ADSearchBase -Filter $ADFilter
foreach ($ADComputer in $ADComputersList)
{
Write-Output $ADComputer.Name
Try
{
$ExplorerProcesses = Get-WmiObject -ComputerName $ADComputer.Name -Class win32_process -Filter "Name='explorer.exe'" -ErrorAction Stop
}
Finally
{
If ($?)
{
foreach ($ExplorerProcess in $ExplorerProcesses)
{
Write-Output " $($ExplorerProcess.GetOwner().User)"
}
}
Else
{
Write-Output " <<< Could not connect"
}
}
}
}
Get-LoggedUsersOnComputers
If you have any remark on my script, please, let me know. I will be happy to make it more cute 🙂
I was playing today with new feature called PowerShell Web Access. This feature was brought in Windows Server 2012. It is very easy to install and easy to use. You need to select one server which will act as Web Access PowerShell gateway server. You will be connecting to this server using SSL and this server will use PowerShell remoting to access computers inside your network. So let’s make it work.
First you need to run PowerShell as a admin on gateway server:
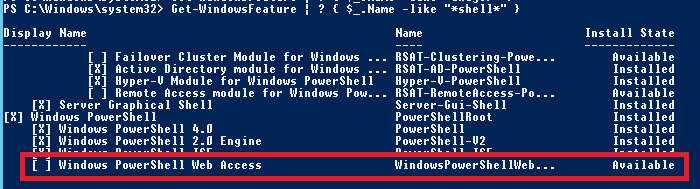
Let’s look for Windows features which contain word “shell”:
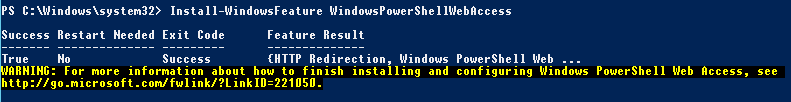
Windows PowerShell Web Access is the feature we want to install. So let’s install it:
Now we can look at this website to lear more, but let’s play more. Now we have new cmdlets containig word “pswa” (PowerShell Web Access):
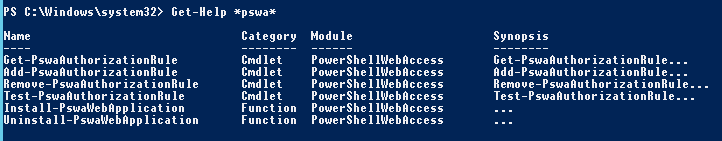
We installed pswa feature, but this feature didn’t install its web component into the server. So let’s install pswa Web application using cmdlet Install-PswaWebApplication with parameter -UseTestCertificate. This parameter creates self-signed SSL certificate for this new site, you can use your own certificate. Be aware that this certificate expires in 90 days.
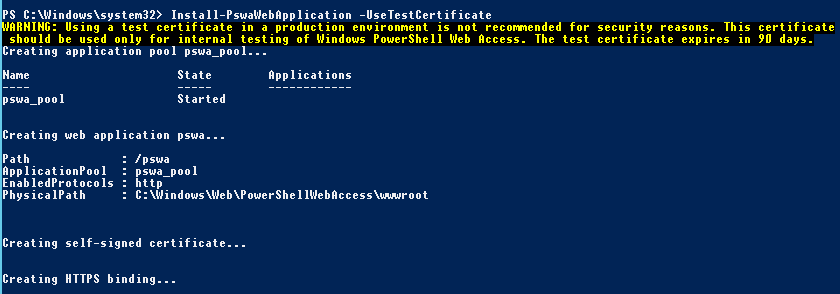
New website was created:
By default no one can use Powershell access gateway. You need to define explicit rules who, where and what can do. For easy test you can use following rule for domain group called GRP_PowerShell_Remote to access all computers with all permissions:
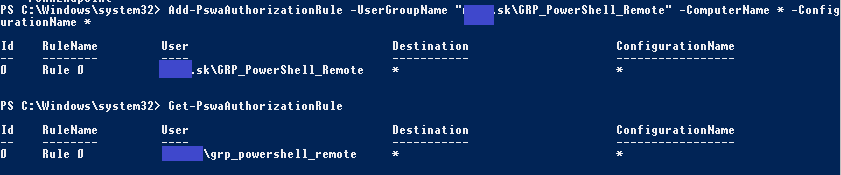
Now everything is prepared. We need to make some changes in network (routers and NAT) to be able to access 443 port on server from Internet. Now when we open site, we can see:
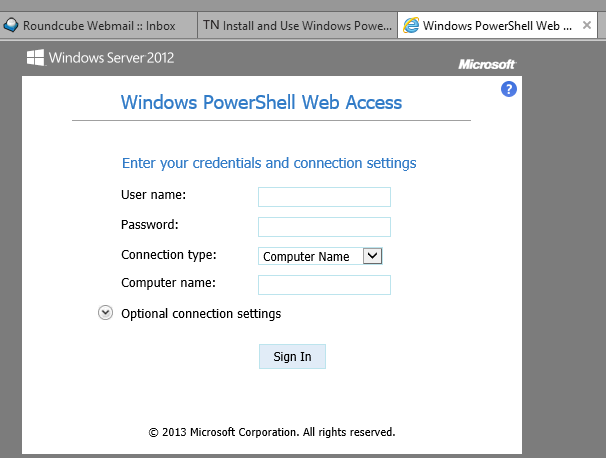
And now you can work on machines inside your network. It’s secure and reliable:
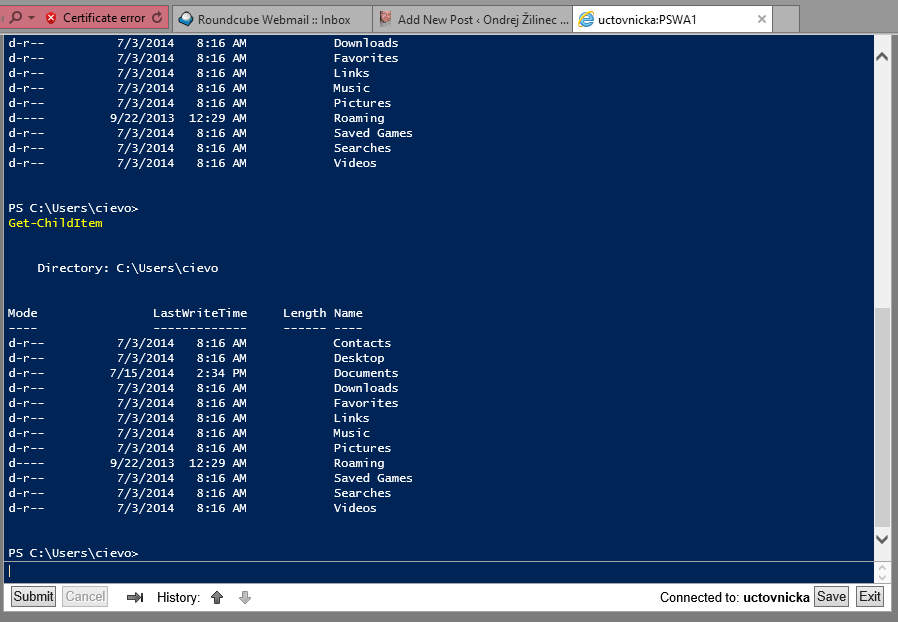
This is very nice and cute feature.
I hope you will start to use and enjoy it.
Have a nice day.
Hello folks
Today I found one really nice utility at Windows Server 2008 R2 and up. It’s called Storage Explorer. It’s MMC snap-in which enables you to see what your fiber optic cards (HBAs) on fiber optic fabrics.
You can see information about your HBAs:
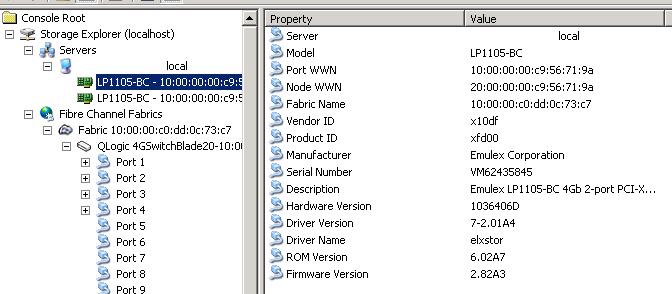
This utility somehow connected into fibre optic switch and listed its ports and WWNs connected to it:
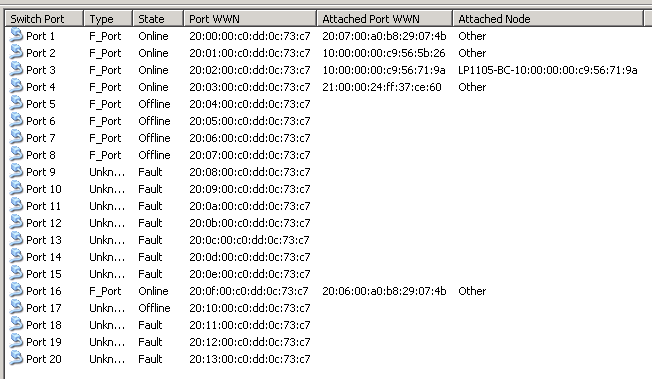
And also found some information about optical switch (for example management IP address):
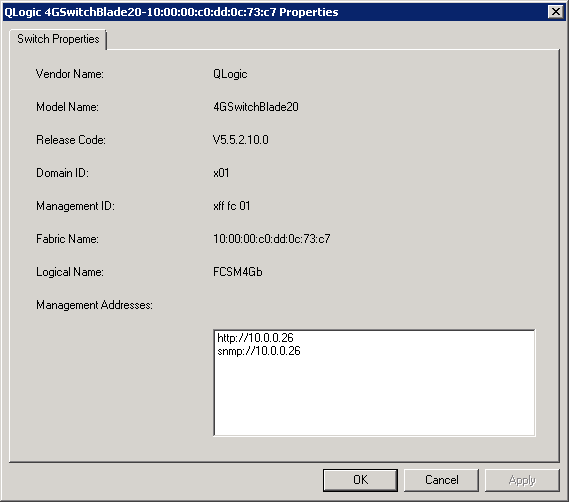
I know this tool is not as powerfull as Brocade SANHealth, but it’s bettern than nothing 🙂
That’s all folks for today,


















Recent Comments