Today I was wondering why I don’t see any updates for Lync Server on Windows Update webpage. After couple minutes I found out article about LyncServerUpdateInstaller.exe. This little (50MB) utility will do updates for Lync Server.
Warning: This utility will not patch database. You need to use Install-CsDatabase instead as described in articles published with updates, which update database.
Today I started installation of Standard version of Microsoft Lync server. There are some prerequisites for OS where Lync server will run. Here is a quick step-by-step howto:
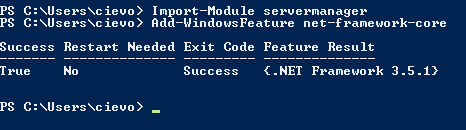
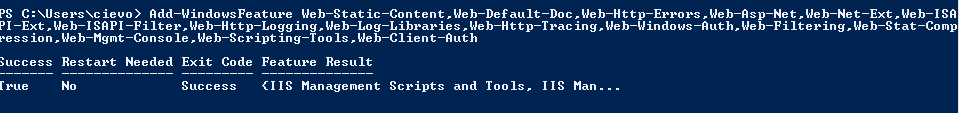
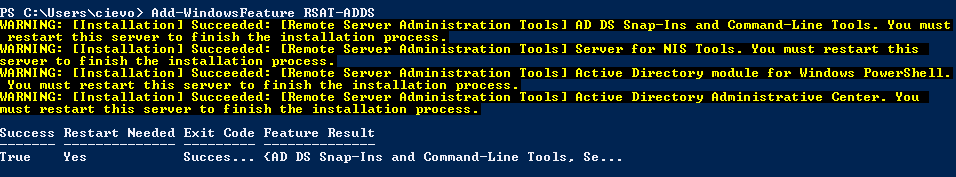
- Install RSAT-ADDS by running following command in same Powershell windows:
- Add-WindowsFeature RSAT-ADDS
- Reboot server
- We need to install Windows Media Format Runtime. We can do it by running following command from elevated command prompt:
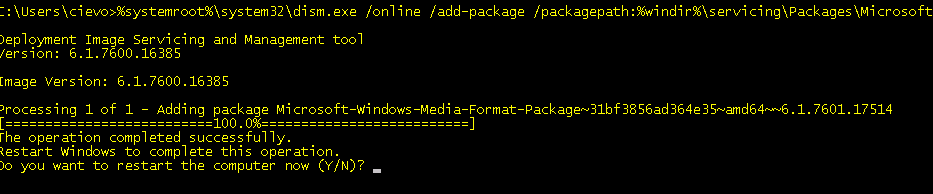
- Press “Y” to reboot server again.
Tomorrow we will prepate Schema, Domain and Forest to support Lync 2010.
Today I connected to Windows 2012 server an notices weird little arrow in the left upper corner (full screen):
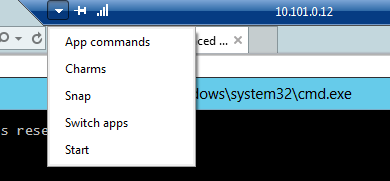
Maybe this will be usefull for some people. I can use only “Start” 🙂
You can access same Remote commands even not in Full Screen RDP:
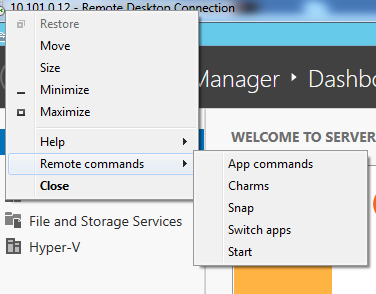
Enjoy,
Problem
Today I was at one customer which recently installed TrendMicro Worry-Free Business Security solution. It’s firewall and anti-* product. Today I noticed there is no free space on C:\ disk. Trend Micro ate 19 GB! The biggest portion of space was located at C:\Program Files\Trend Micro\Security Server\PCCSRV\Log. There were files called ofcdebug-*.log which were about 150 MB of size and there was lots of them. And there new comming and comming 🙂
Solution
Those file are debugging log files. There is really weird way to disable them. In management website you need to click on little small letter “M” in the logo:
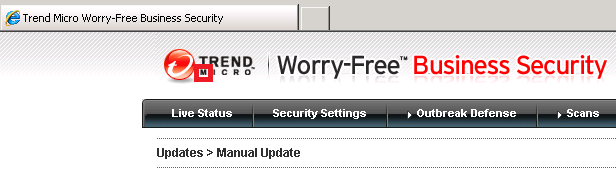
New window appears where you can enable/disable debug logs:
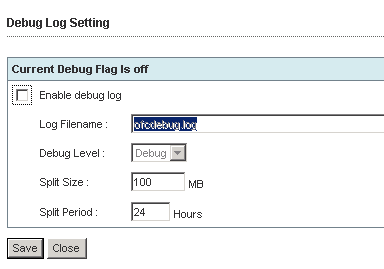
This is really weird way to set logging by looking for some small letter “M” 🙂
More about it on official site.
ShowIT-BrachCache_Zilinec
Ak by ste mali nejaké otázky, sem s nimi.
You can configure expiration period for Certification Template. By default there are default maximum validation periods set to:
This means you have Certification Template set its validity for example for 10 years, but you can enroll certificates with validity 1 or 2 years (Stand-alone / Enterprise Certification Authority).
This can be changed via registry keys described in KB254632.
Thank you for my colleague Róbert Švec.
When administrators implement Roaming Profiles they define folder where roaming profile should be stored on fileserver. By default file permissions for the newly generated profile are full control for the user, full control to SYSTEM and no file access for the administrators group. You can not access this profiles with administrator account and clean it up. First you had to take ownership and then you can change ACL, but this is not what you want, because owner should be user.
You can fix this in two steps:
New roaming profile folders
You can change default behaviour on new profile folder creation. It can be changed by applying GPO to domain controllers with following setting Enabled:
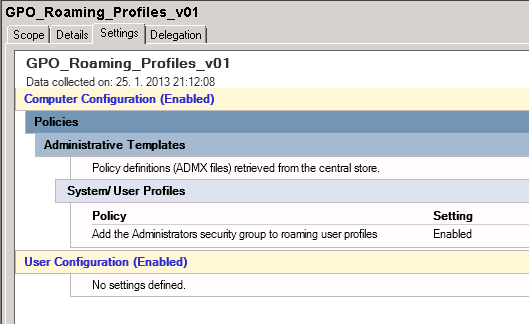
Change ACLs for existing profile folders
This will be in couple steps:
-
- Download PsExec
- Log into fileserver where profiles are stored
- Run cmd.exe under SYSTEM account by running command
psexec -sid cmd.exe
- In new cmd.exe window go into directory where roaming profiles are stored. For example: cd G:\Profiles\
- Add BUILTIN\Administrators into ACLs of roaming profiles by running following command:
subinacl /subdirectories=directoriesonly G:\Profiles\*.* /GRANT=Administrators=F
Enjoy accessible roaming profile folders 🙂
Couple months ago we have created Active Directory domain for one of our customer. His AD was subdomain of existing AD domain hosted in Germany. Let’s call them following:
- DOMAIN.LOCAL <– Main AD in Germany
- SK.DOMAIN.LOCAL <– New created domain in Slovakia
To make administrators life easier in future, we have created DFS Shares in domain SK.DOMAIN.LOCAL. One of those DFS shares is called “Common”. So people in Slovakia were accessing DFS share \\\\SK.DOMAIN.LOCAL\\Common and share data. Under this DFS Namespace following share was hidden \\\\FSSERVER\\Common.
Everything worked just fine.
Problem
Problem appeared when users from Germany (from domain DOMAIN.LOCAL) wanted to access this share. There were following symptomps:
There were no firewalls between two domains. All ports were accessible.
Solution
After couple tries (and using dfsutil) I figured out that client machine from DOMAIN.LOCAL get as DFS Refferal NetBIOS server name FSSERVER and it cannot translate FSSERVER to IP (FSSERVER is from SK.DOMAIN.LOCAL). Client machine from DOMAIN.LOCAL although can translate FQDN of FSSERVER.SK.DOMAIN.LOCAL. I tried to put FSSERVER IP record into client machine’s hosts file and everything started to work perfectly. So we have more solutions to solve issue:
I decided to force DFS to propagate FQDN as refferals. It’s made by change in registry keys for DFS service. More about it is at http://support.microsoft.com/kb/244380/en-us. One more important thing is that you need to remove and re-add refferal servers from DFS Namespaces. I used DFS console because I didn’t use DFS Replication. If you do use DFS Replication it’s recommended to do it using cmd line (dfscmd.exe).
That’s all folks,
More often I see people (IT admins) not understand differences between Local Service Accounts so I decided to write more about it:
SYSTEM
This account has full access to local computer. It can access network resources with rights (account) of the computer. This account has full access to domain it self when used on Domain Controller.
LOCAL SERVICE
This account has same right as local Users group. It goes to network as annonymous user (null session).
NETWORK SERVICE
It’s almost same as LOCAL SERVICE. Only difference is that it uses computer account to access network resources.
I was just browsing Internet a looking for built-in utilities in Windows. I found one nice one getmac.exe which can get the list of MAC addresses on local or remote computer. It’s nice utility and it’s better to use it to find out MAC addresses, because looking into ipconfig /all verbose output is very time consuming (look in it when IPv6 is enabled). 🙂
Also ipconfig cannot be run on remote machine without using other utility (for example psexec).
More information here.









Recent Comments