Prisiel ten cas ked je Windows 10 vonku a vela ludi sa chysta na migraciu. Danu aktualizaciu z Windows 8.1 na Windows 10 som absolvoval aj ja. Ak sa vam nechce cakat na to, aby vas vas operacny system vyzval k danej aktualizacii, tak si mozete danu aktualizaciu vynutit. Vynutit sa da stiahnutim cca 20 MB suboru z tejto stranky.
Spusti sa vam sprievodca, ktory vam ponukne stiahnut data pre vytvorenie DVD/USB media alebo spustenie aktualizacie. Ja som sa rozhodol spustit aktualizaciu. Stahovalo to cely windows na C: disk:
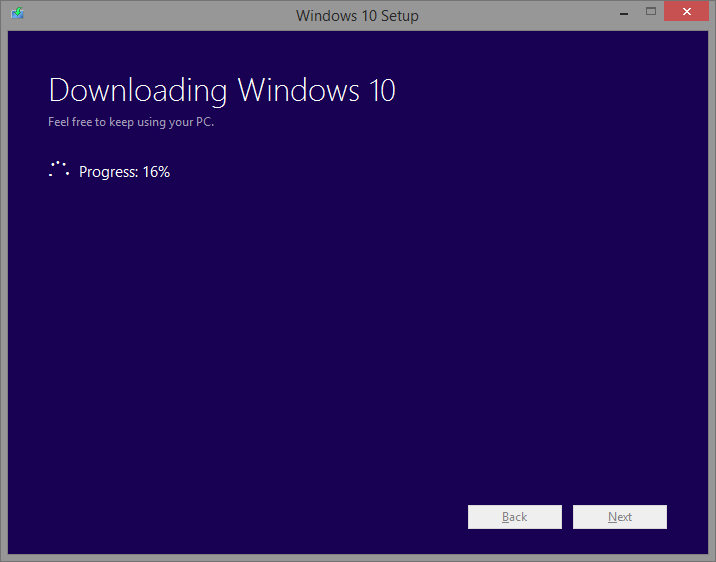
A nasledne sa spustila aktualizacia. Lenze mna zarazilo nasledovne okno:
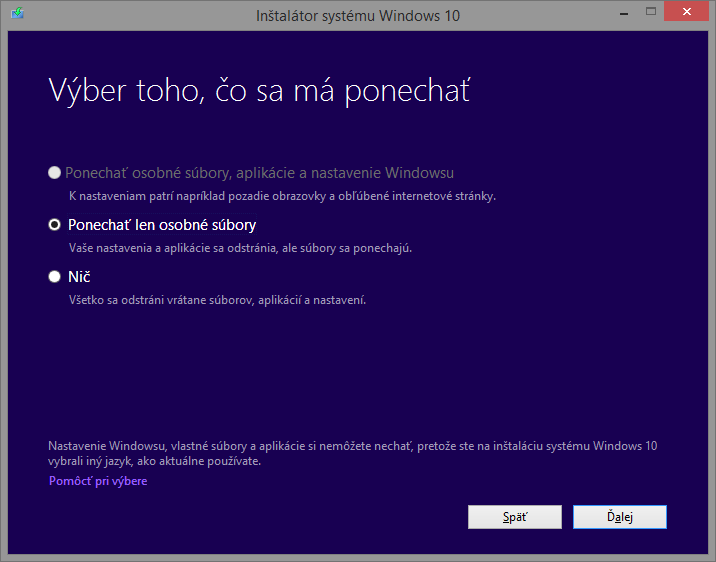
Mozno cislo jedna bola vysedena a nebolo mozne ju vybrat. Microsoft, bohuzial, dovoli pouzit prvu moznost len pre Windowsy, ktore su v jazykoch: Anglicky, Brazilsky, Portugalsky a jednoducha Cinstina. Je to smutne ale je to tak. Skusal som zeditovat aj instalacku a jej nastavenia ale nic nepomohlo. Taktiez som skusal zmenit nastavenia Windowsu na inu ako Slovensku lokaciu a taktiez nepomohlo. Vyzera, ze pri stahovani aktualizacie si dana aplikacia stiahla slovensku verziu aktualizacie a aj instalacky:
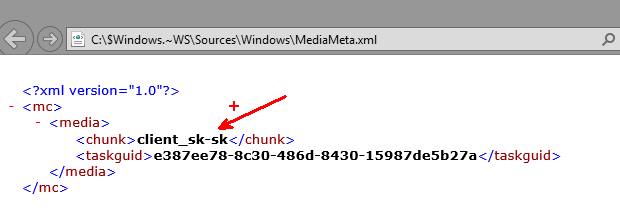
Takze neostavalo nic ine ako ist na tuto stranku a stiahnut anglicku verziu instalacky. Ked sa po stiahnuti dana instalacka pustila, tak vsetko slo ako po masle:
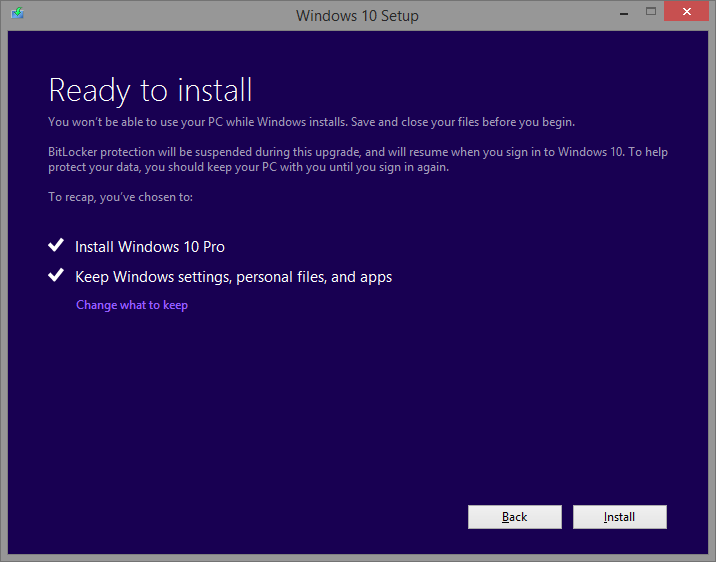
Vsetky nastavenia mi ostali. Par aplikacii bolo potrebne preinstalovat (VPN klienti) ale inak vsetko funguje ako ma a uz fungujem na Windows 10:
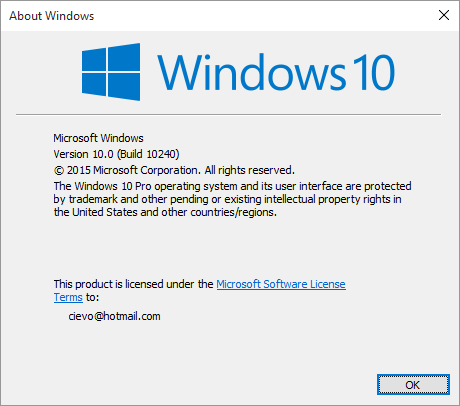
Nemam odskusane ci pri instalacii anglickej verzie Windows 10 sa zanecha slovenske prostredie alebo treba este doinstalovat slovencinu.
Dufam, ze dany navod pomoze niekomu dalsiemu 🙂
Customer requested to force active directory accounts to expire on midnight or in the night and not during the day. So I’ve created following script to do so:
$UserList = Get-ADUser -Filter * -SearchBase "OU=USERS,DC=domain,DC=local" -Properties "DisplayName", "PasswordLastSet"
$Today = (Get-Date)
$MaxPasswdAge = (Get-ADDefaultDomainPasswordPolicy).MaxPasswordAge
ForEach ($User in $UserList)
{
$ExpireDate = ($User.PasswordLastSet) + $MaxPasswdAge
$DaysToExpire = (New-TimeSpan -Start $Today -End $ExpireDate).Days
If ($DaysToExpire -eq 1)
{
Set-ADUser -Identity $User -ChangePasswordAtLogon $true
}
}
#EOF
This script runs everyday at 23:55.
I found couple examples how to change pwdLastSet attribute on AD user’s object, but I don’t like that. I think this is cleared way to do so.
Have a nice day,
I migrated from Exchange 2003 to Exchange 2010 and since then I was receiving following event:
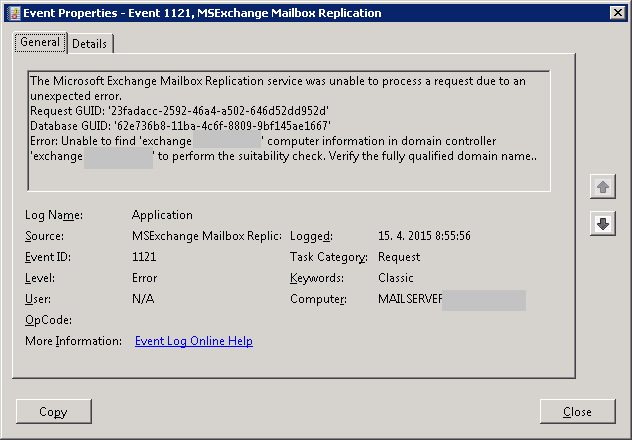
Event says:”The Microsoft Exchange Mailbox Replication service was unable to process a request due to an unexpected error”. Which means server cannot finish some request. In order to solve a problem I was looking for some replication settings. I found none. Then I looked into domain using ADSIEdit. I looked into:
CN=MailboxExportRequests, CN=MailboxReplication, CN=TeamSK, CN=Microsoft Exchange, CN=Services, CN=Configuration, DC=domain, DC=local
and I found there some old orphan move requests:
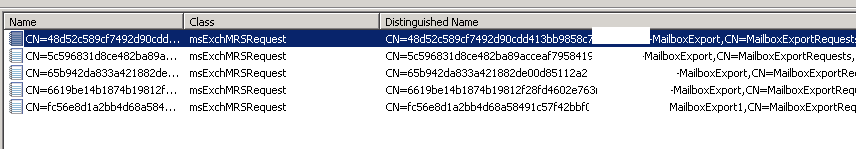
When I used Get-MoveRequest cmdlet there was none move request displayed. So I’ve deleted those old move requests using ADSIEdit and there was no more bothering event on Exchange server.
Have a nice day,
When you export certificate in Windows with private key, you export it to .pfx file with password. When you want to use this certificate in linux you need to convert pfx file into .crt and .key files. You can use following commands to convert it:
[root@nagios]# openssl pkcs12 -in nagios.pfx -clcerts -nokeys -out nagios.crt
Enter Import Password:
MAC verified OK
[root@nagios]# openssl pkcs12 -in nagios.pfx -nocerts -nodes -out nagios.key
Enter Import Password:
MAC verified OK
Now you have two files .crt and .key which can be used in linux.
That’s all folks,
This is just a note. When you have UAC (User Access Control) enabled and if application wants to write data into %ProgramFiles% all writes are redirected into %localappdata%\virtualstore\. If application writes into registry HKLM\Software it is redirected to HKCU\Software\Classes\VirtualStore.
That’s all folks,
I am often asked to restore files on fileservers and also look for user who deleted files. By default there is no auditing for files enabled on fileservers. I will write how I do enable it and how it works for me.
First of all you need to enable audit policy Audit object access. This audit policy handles auditing for files, registry keys, shares, … To enable this audit policy you need to set it in GPO Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Local Policies – Audit Policy – Audit object access and set it to Success, Failure.
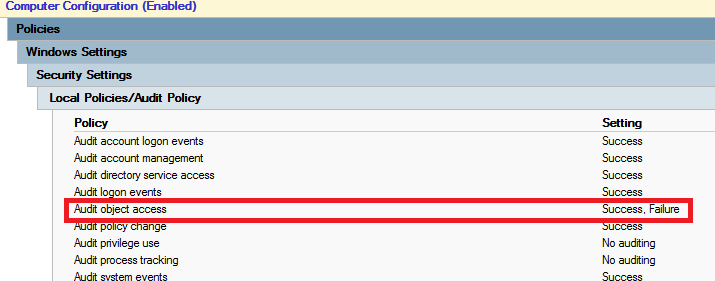
This audit policy enables auditing for lots of objects to audit. I want to audit only File System. To find out what audit policy settings are applied on computer use following commnad auditpol.exe /get /category:*. To enable only wanted auditing I have dumped settings using auditpol.exe command and set same auditing in GPO, but under Object Access I just enabled File System auditing. You can set this settings under Computer Configuration – Policies – Windows Settings – Security Settings – Advanced Audit Configuration.
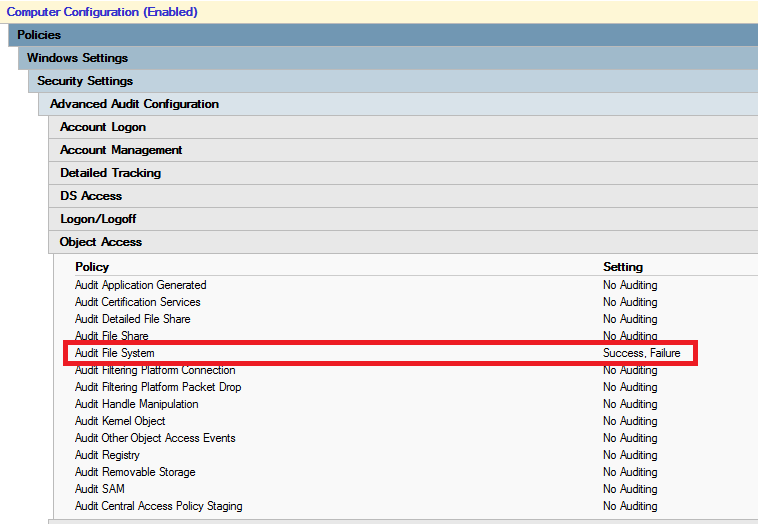
Now you need to setup Auditing on whole Disks or Folders:
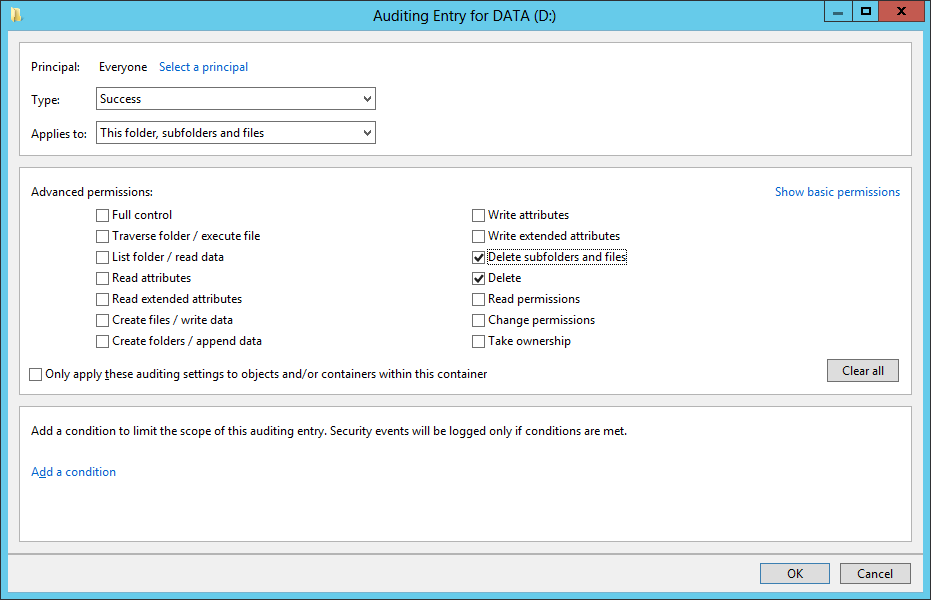
When these settings in GPOs are applied there are new events in security event log. We need to look for event number 4659 and make some reporting out of it. I’ve created powershell script which I run every day right after midnight and it creates HTML report and also CSV files which can be used in some powershell manipulation. Here is a powershell script:
#
# Get-DeletedFileLog
# This function gets events 4659 about delted files and generate HTML reports
#
#
# Declaration
#
[datetime]$Yesterday = ((Get-Date) - (New-TimeSpan -Day 1)).date
[datetime]$Today = (Get-Date).date
[int]$EventID = 4659
[string]$Path = "D:\Logs\Deleted Files"
[int]$Limit = (Get-Date).AddDays(-180)
Try
{
#
# Get events from security eventlog
#
[array]$EventList = Get-WinEvent -FilterHashtable @{Logname='Security';Id=$EventID;StartTime=$Yesterday} -Oldest -ErrorAction Stop
#
# Extend Event by XML data fields
#
foreach ($Event in $EventList)
{
$EventXML = [xml]$Event.ToXML()
For ($i=0; $i -lt $eventXML.Event.EventData.Data.Count; $i++)
{
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name DateFileDeleted -Value $Event.TimeCreated
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name UserName -Value $EventXML.Event.EventData.Data[1].'#text'
Add-Member -InputObject $Event -MemberType NoteProperty -Force -Name DeletedFile -Value $EventXML.Event.EventData.Data[6].'#text'
}
}
#
# Generate HTML report
#
$EventList | Select DateFileDeleted, UserName, DeletedFile | ConvertTo-Html | Out-File "$($path)\$($Today.Year)$($today.Month)$($Yesterday.Day)_DeletedFiles.html"
$EventList | Select DateFileDeleted, UserName, DeletedFile | ConvertTo-Csv | Out-File "$($path)\$($Today.Year)$($today.Month)$($Yesterday.Day)_DeletedFiles.csv"
}
Catch
{
# If there is a problem
Write-Host "No events $EventID to record."
}
#
# Remove old reports
#
Get-ChildItem -Path $Path -Recurse -Force | Where-Object { !$_.PSIsContainer -and $_.CreationTime -lt $Limit } | Remove-Item -Force
# EOF
This script also cleans up files older than 180 days. In HTML file you can see when, who and what deleted. I didn’t excluded files started with “~”, which are also known as temporary Office files, which are created during opening Office documents. This is because now I know who opened which files and when.
Enjoy,
At one of our customers we deployed RDS RemoteApp server farm. Customer bought thin clients HP T510. When they connected to RemoteApp using Windows XP and Windows 7 on normal computers there were no problems with RemoteApps. When they connected to RemoteApp using Windows 7 Embedded on thin clients, they had problems with RemoteApp windows. RemoteApp windows were not displayed right. There was one extreme problem: User opened Microsoft Outlook, opened message and pressed Reply. Starte to type, but no characters were displayed. When you clicked on some part of the window all the text appeared. So RDP client sent all key strokes to RDP server, but RDP client didn’t refresh content of the window.
After some investigation I found out that Windows XP and Windows 7 had RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported), but Windows 7 Embedded had only 6.2.9200 (RDP 8.0 supported). I’ve tried to google for some path or some HP image with RDP 8.1 for Windows 7 Embedded. No success. When you look on Remote Desktop Service Blog website, you can even find informaction that there is no RDP 8.1 for Windows Embedded.
But I found five hotfixes which are required for Windows 7 Emedded to have RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported):
- KB2574819-v2-x86
- KB2592687-x86
- KB2857650-x86
- KB2830477-x86
- KB2913751-x86
When you install all those updates you need to reboot machine and you will have nice RDP client version 6.3.9600 (RDP 8.1 supported):
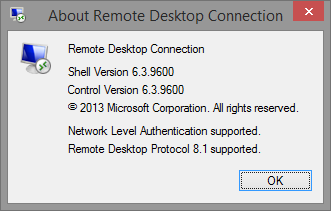
That’s all for now,
Sometimes I need to run some command on bunch of computers. So I’ve created little bit more advanced function to be able to run script block on computers list created from domain:
<#
.Synopsis
This function provides you way to run scriptblock on remote machines in the domain.
.DESCRIPTION
This function is extension to Cmd-Let Invoke-Command. This function lists computer names in domain
based on ADSearchBase and Filter parameters. In invoke scriptblock on those computers in the list.
.EXAMPLE
To restart service "Windows Time" on all machines in domain:
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase "DC=domain,DC=local" -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
.EXAMPLE
To restart service "Windows Time" on all machines which containt number 7 in name:
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase "DC=domain,DC=local" -Filter 'Name -like "*7*"' -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
#>
Function Invoke-CommandOnADComputers
{
[CmdletBinding(SupportsShouldProcess=$True,ConfirmImpact='Low')]
Param
(
# This is Active Directory Search Base to limit selection for computer accounts in domain.
# It can be for example "OU=Computers,OU=Company Name,DC=domain,DC=local"
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[string]
$SearchBase,
# Active Directory filter to merge your computer selection in to the detail.
# It can be for example 'Name -like "Desktop*"'
[string]
$Filter = "*",
# This is scriptblock which should be run on every computer.
# For example { Restart-Service W32Time; }
[parameter(Mandatory=$true)]
[scriptblock]
$ScriptBlock
)
Begin
{
#
# Get list of computer accounts
#
Write-Verbose "Getting list of computer from $ADSear"
try
{
[array]$ADComputersList = Get-ADComputer -SearchBase $SearchBase -Filter $Filter -ErrorAction Stop
}
catch
{
Write-Error -Message "Couldn't search in $SearchBase" -ErrorAction Stop
}
#
# Write number of found computers
#
Write-Host "Found $($ADComputersList.Count) computers"
#
# If in debug, write list of computers
#
Write-Verbose "List of machines:"
If (!$PSDebugContext)
{
foreach ($item in $ADComputersList)
{
Write-Verbose " $($item.Name)"
}
}
Write-Verbose "Done with domain computer list"
}
Process
{
#
# Let's invoke command on remote computer
#
foreach ($ADComputer in $ADComputersList)
{
Write-Host $ADComputer.Name
try
{
Write-Verbose "Invoking scriptblock on computer"
Invoke-Command -ComputerName $ADComputer.Name -ScriptBlock { $ScriptBlock } -ErrorAction Stop
Write-Host " Scriptblock invoked successful."
}
catch
{
Write-Host " Scriptblock invoked UNSUCCESSFUL."
}
}
}
}
You can run it using
Invoke-CommandOnADComputers -SearchBase “DC=domain,DC=local” -ScriptBlock { Restart-Service W32Time; }
and it will read all computer accounts from domain and restart Windows Time service.
Enjoy,
If you want to know if your computer is ready to host Hyper-V role you can check it quickly using old command systeminfo.exe with new feature. This new feature is in systeminfo.exe which is included in Windows 8 and higher and Windows Server 2012 and higher.
When you run it you can see the last output lines about Hyper-v Requirements:
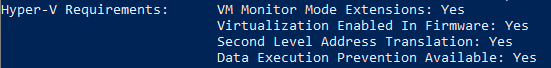
That’s all for today,












Recent Comments