SYSVOL FRS to DFSR migration
Most of you probably already updated Active Directory infrastructure from Windows 2003 to Windows 2008 R2. What I see most is that administrators do not upgrade DFS replication subsystem for SYSVOL shares. Before Windows Server 2008 (also R2) was released FRS (File Replication System) is used. In Windows 2008 R2 there is new version released and it’s called DFSR (Distributed File System Replication).
FSR
FSR uses NTFS volumes’ USN journal to determine when a change has occured to a file and triggers replication. When FSR detects file close it gathers information about file and it’s attributes. It also checks file’s MD5 hash. If MD5 hash changes it will trigger replication. If file has changed whole file is send to FSR replication partners.
DFSR
First benefit of DFSR is that it doesn’t replicate whole file, but just a changed data in the file. To be able to check only changes in files it uses RDC (Remote Differential Compression) compression algorithm.
Migration in theory
To be able to use DFSR two conditions have to be met:
-
All domain controllers have to be at least Windows Server 2008
-
Active Directory domain level has to be at least Windows Server 2008
Migration is divided into stable and transition states. Stable states are:
-
Start – It’s a state before whole migration
-
Prepared – FSR replicates SYSVOL, while DFSR replicates SYSVOL content into its directory
-
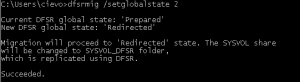
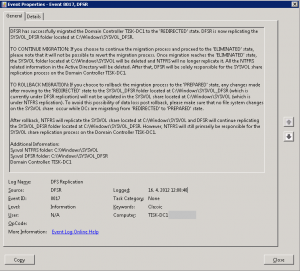
Redirected – DFSR copy of SYSVOL is shared to users. FSR replicates original SYSVOL and DFSR replicates copy of original SYSVOL
-
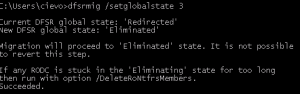
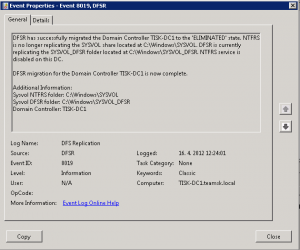
Eliminated – DFSR takes care of SYSVOL share completely and FSR no longer replicates SYSVOL data
In background whole migration tool does following:
-
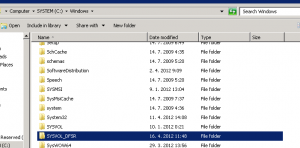
creates directory C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr
-
copies data from C:\\windows\\sysvol into C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr
-
remaps share SYSVOL into new directory C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr
-
deletes original directory C:\\windows\\sysvol
Before migration it’s important to have healthly AD infrastructure with working replication. You can check your infrastructure by:
-
checking SYSVOL share via net share command
- using utility Ultrasound
-
checking with repadmin /replsum
Migration in practice
I will do the migration in one of my customer. Shares at customer site look fine:
Stage Start –> Stage Prepared
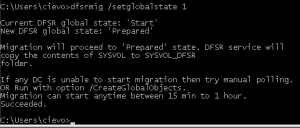
This is very simple. You need to run command:
dfsrmig /setglobalstate 1
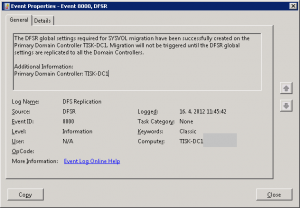
Also event in DFS Replication eventlog was recorded:
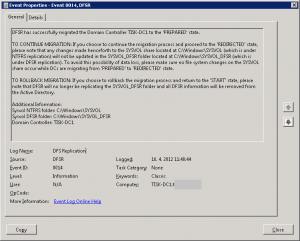
and couple more events and the last one is
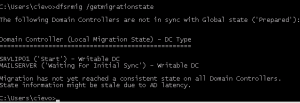
You can check other DC by running command:
dfsrmig /getmigrationstate
and you get following output (AD not in consistent state yet):
When it’s ready you will see following:
When server is ready you can find directory C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr:
Stage Prepared –> Stage Redirected
Just another easy step. Run following command:
dfsrmig /setglobalstate 2
And again you can check other DC by running command:
dfsrmig /getmigrationstate
When it’s all done, you will see following message:
And also SYSVOL and NETLOGON share are redirected to new directory C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr:
Also Event is saying details about changes:
When everythin looks fine, let finish it up.
Stage Redirected –> Stage Eliminated
This stages eliminates FSR from replicating SYSVOL data. Now you have to check your replication really close, because there is no step back.
If everything is alright, run following command:
dfsrmig /setglobalstate 3
When it’s done you will see running
dfsrmig /getmigrationstate
and also see following event:
There is no more C:\\windows\\sysvol directory. Just brand new DFSR directory C:\\windows\\sysvol_dfsr.
If you don’t use FSR services for any other replication you can remove it from your servers by removing File Replication Service.
I hope this arcite helps to keep your infrastructure up to date and use the goodies what new stuff brings.
There are usefull utilities to manage/debug DFSR: DFSRADMIN, DFSRDIAG, DFSUTIL, DFSCMD and DFSDIAG.
Is any command that shows you which protocol (FRS or DFSR) are you using for SYSVOL replication?